Introduction
Accounting and Taxation is defined as a branch of “finance” that applies to all individual and business. There are normally two set of principles that are mainly seen in the perspectives of accounting. The first comes the “tax accounting” and the next that is seen is “financial accounting”. These “accounting procedures” are all followed under “GAAP”. The “Generally Accepted Accounting Principles” says that the companies must follow a common set of “accounting principles” and “standards” which are used in the “compilation” of the “financial statements” including the “transactions”. On the other hand for an “individual tax payer” the main focus is to determine income that would help the individual in “qualifying deductions” and at the same time would help to get an “annual tax return”.
Top 30 Accounting and Taxation Questions and Answers
Q1. Give your Introduction
This question may seem easy but answering this in an effective way is the most important thing. The candidate should make the “first impression as the last impression”. Delivering the introduction in right wat would help to “secure and acquire” the desired job. While giving an introduction the candidate should “initiate” proper conversation showing deep interest in “accounting and taxation”. You should be able to make the interviewer interested about how “accounting and taxation” have become your sole passion. It is important that you impress the “employer” with the correct approach.
Q2. Tell me about the different types of accounting.
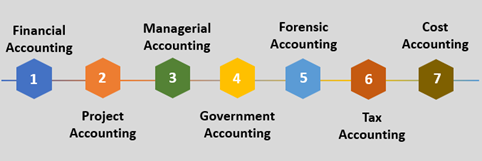
The different types of accounting are:
- “Financial Accounting”
“Financial Accounting” records information related to the “financial status” of the company. This is identified to be a “branch of accounting” that involves measuring, recording, “analyzing” and “classifying” the business transactions.
- “Administrative Accounting”
This type of accounting focuses on the “administrative aspects” of the company. “Administrative Accounting” is considered to be very useful in making accurate “plans and actions” which are used to fulfill the objectives of the company including the “improvement of strategy” of a company.
- “Cost Accounting”
This type of “accounting” is focused on certain companies that have an “industrial nature”. This accounting takes care of the “unit cost of production”. It helps in analyzing the “sales and production process” that a company mainly carries out.
- “Tax Accounting”
This “accounting” focuses on the “registration and preparation” of reports that concern with “tax return and tax payments”. “Tax Accounting” is mainly used by the individuals, business and corporations”.
- “Management Accounting”
“Management Accounting” is an expanded version of “cost accounting”. This records all the “financial and economic information”. The perspectives of “management accounting” measures all “long-term and short-term finance” related decisions.
Q3. What is “Tax”? Why you think it is “imposed and collected”?
“Tax Specialist” is defined as the “charge” that is mainly “levied” by the government. This word is mainly derived from the Latin word “tax” that is mainly carried out to realize the “public expenditures” which cater to “social welfare aspects”.
The payment of “tax” is mandatory and it also serves to be the main determinant of “mandatory contributions” which is to be made by the “individual or any organization”.
Taxes are “imposed and collected” for the following reasons:
- “Taxes” are used to “raise revenue”. Through the process of “collection of tax” “finances” are needed for the “provision of basic services” that are mainly meant for the general “administrative purposes”. It also focuses upon the process to “finance the capital projects”.
- “Taxes” help in the correction of “unfavorable balance of payment”. It is upto the government to decide the terms that can increase the “tax rate” on these goods.
Q4. What is Taxation?
This “Accounting and Taxation” question is the most important one. “Taxation” is the process to impose or “levy” taxes that are framed by the government. It is mainly “imposed” on the “individual and business entities”. “Taxation” ranges from “income tax to goods and services tax” which applies at all levels.
Recently the government has brought about different “progressive policy reforms” that has informed changes into the existing process of taxation.
To make the process of “taxation” innovative and efficient several changes have been adopted within the system which has “eased the system of sales” and the supply of goods.
Q5. What is “Direct and Indirect Tax”?
This “Accounting and Taxation” question deals with the aspects of “direct and indirect tax”.
“Direct Tax”, is mainly “levied” by a person or a property over their profits. The company which has a certain responsibility to “pay tax” would “pay” directly to the government. Some of the examples of “direct tax” are:
- “Tax” includes “salary and other sources” of income.
- “Gift Tax”.
- “Fringe Benefit Tax” which is mainly paid by an employer concerning the “employees” over the “fringe benefits provided”.
“Indirect Tax” is generally collected from the third person. It mainly relates to the consumers who have to pay for the “goods and services” and the “manufacturers”.
The recent “tax reforms” have “overhauled” the taxation system of India. This has brought the concepts of “ONE NATION ONE TAX” regime that is also called as the “Goods and Services Tax”, which came into effect on July 1, 2017.

Q6. How to maintain accuracy in “accounting”?
“Accounting and Taxation” accuracy cannot be maintained. In fact they are held to be “reasonable” depending upon facts. There are “accruals”, “prepaid”, “deferrals” which are involved in the process of “accounting”. The use of “accounting” does not guarantee the accuracy of the data maintained. The main fact that lies are the existence of the “accounting standards” which are considered while calculating the estimates.
Q7. What is “Working Capital”?
This “accounting and taxation” interview question deals with the concept of “Working Capital”. It is defined as the difference between “current liabilities” and “current assets”. If the process of determination of “working capital’ is simple then it mainly focuses upon the “capital resources” of the company which the company “counts” on a “short term basis” to look after the operations that it holds.
These resources mainly include the “cash”, “portfolio of the finance related products” and the other investments that the company holds.
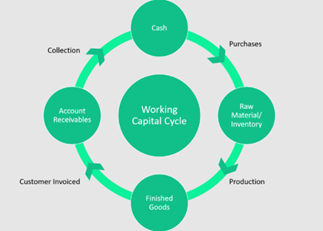
Q8. How can you improve the “Working Capital Flow” of a company?
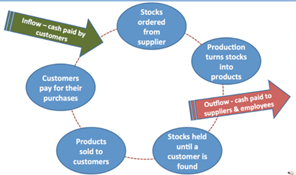
This “accounting and taxation” question deals with the suggestions of how the existing “Working Capital Flow” of a company can be improved. The best way to improve the “working capital flow” of the company is to consider the existing “stock in hand” of the organization. The “stock” that a company mainly holds is the main component of the “working capital” which can be controlled.
For this the “debtors” are pressurized to “pay back the debts” quickly. This process does not guarantee any control over the “payments” as these are identified to be “separate legal entities”.
The business at this stage can stop the payment to be made to the “suppliers”, but doing this it can ruin the “business relationships” and at the same time can ruin the “reputation” of the company. This is the reason which determines not to “hold back” the money that is “due” on the “supplier’s side”.
The business needs to understand that “funds” present in the company always “come at a cost” and thus it is the duty of the organization not to only stick to the “stocks”. The business must keep this in mind that “overvaluation of stock” should be avoided and on this contrary the “stock turnover rate” should be high so that the “working capital” can be in a better position.
Q9. What do you mean by Income Tax?
This “accounting and taxation” interview question deals with the concepts of “Income Tax”. This is mainly a “direct tax” that is imposed on every “taxable individual”. The “imposition” deal with different rates that are ensured within their own “jurisdictions”. The person “liable to pay tax” has to “file the returns” on an annual basis that would be able to meet the respective “tax obligations”. The income concerning every person should be calculated under different heads such as:
- “Salary”
- “Wages including dividends and interest”.
- “Rental Income”.
- “Income from Property”.
The “income tax” also covers the “estimated tax slabs” which are calculated in their respective percentages. These are:
- For income ranged between “5 lacs to 7.5 lacs”, the estimated percentage applicable is 10%.
- For the income that is between “7.5 lacs to 10 lacs”, the applicable percentage is 15%.
- The income ranged between “10 lacs to 12.5 lacs”, the percentage applicable is 20%.
- The income which falls between “12.5 lacs to 25 lacs”, the applicable percentage is 28%.
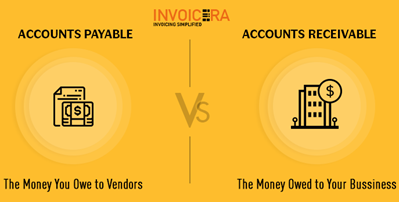
Q10. Differentiate between “Accounts Payable and Accounts Receivable”
“Accounting and Taxation” have an important feature which is known as the “accounts payable”. It is the amount of money that a company holds. It mainly includes the “purchases of the goods and services” from the “suppliers”.
“Accounts Receivable” is again an important aspect of “Accounting and Taxation”. It mainly deals with the money which the company has the right to collect in account of the “goods sold” to the final customers on “credit”.
Q11. What are the common mistakes in accounting?
This is an important “accounting and taxation” interview question. The common mistakes in “accounting” are:
- Lack of “backup”.
- “Less Communication, between the accountant and the company”.
- Misallocation of the “resources”.
- “Misplacing” of the receipts.
- “Manual Accounting” process obstructs the efficiency.
- “Accounting books are not kept up to date”.

Q12. What is “GST Council”?
This “accounting and taxation” interview question deals with the “constitutional body” named as “GST Council”. The “Goods and Services Tax Council, GSTC”, is mainly identified as a “legal structure” which looks after the “implementation of GST act” throughout the country. This is mainly dealt under “Article 279A of the constitution”.
Q13. What is “Tax Invoice”?
This “accounting and taxation” interview question deals with the implication of “tax invoice”. This “tax invoice” is mainly referred under “section 31 of the CGST Act, 2016”. This is determined as an “important legal entity” which makes it a “mandate” to the “registered person” to issue “tax invoice” which is mainly meant for the “supply of goods and services”. If in this case the “supply” is done by an “unregistered person” then the “recipient” has to issue the “Bill of Supply” instead of a “tax invoice”.
It is important to also impose the “input tax credit” which has been made to the supplier. It also serves to be an “important evidence” which includes the “charging of GST” at the time of the imposition of “tax invoice” that forms to be an “indicator” of “supply made”.
This contains the name of the “supplier” and also the “recipient” including the “details of the goods”, “quantity” and the value of the other details.
Q14. Are you familiar with the “Accounting Standards”? How many “Accounting Standards” are there in India?
This is a very common question that is asked in the “accounting and taxation” interviews. It is important to have the knowledge of the “International Accounting Standards”. It is normally a vast topic through which the candidate needs to be well versed with the “latest changes”.
Currently there are 41 “accounting standards” in India.
Q15. What is the main difference between “Trial Balance” and “Balance Sheet”?
This “accounting and taxation” interview question deals with the main difference between “Trial Balance and Balance Sheet”.
A “Trial Balance” shows the list of all the accounts which is mainly used to check the “arithmetic accuracy” while recording and “posting” transactions.
On the contrary a “balance sheet” is a statement that mainly displays the “assets and liabilities” including the “equities” of an organization. A “balance sheet” is mainly used to determine the “financial position” of a business.
Q16. What is the importance of “documentation” in Accounting?
This aspect of “accounting and taxation” deals with the documentation. The “accounting” is mainly like a “watchdog” of an organization and this is the reason which makes this system to be very systematic.
The “accounting heads” have the responsibility to determine a “true and fair view” of the “financial statements” of the company which are to be presented to the “stakeholders”.
Documentation serves to be the most important aspect of accounting. For this there is the need to “verify the adequate documents” for which necessary “audit trail” needs to be maintained.
Q17. What is “Composition Scheme”?
This aspect of “accounting and taxation” deals with the determination of the “composition scheme”. This is mainly availed by the “small traders: who have a “turnover” less than “1.5 crore” and want to make themselves free from the “detailed formalities” of paying “GST” at a “fixed turnover”. The “turnover” of the business that is registered under the same “PAN number” is mainly to be taken into consideration.
“Exemptions of the Composition Scheme”
- “Interstate Supplier”
- “Casual Taxable Person”
- “E-Commerce Operators”
Rates of “Composition Scheme Dealers”
- For “manufacturers and traders” the “composition scheme” rate is 1%.
- For “restaurants not serving alcohol”, the “composition scheme” rate is 2.5%.
- For the “other service providers”, the ‘composition scheme” rate is 3%
Q18. What is “e-way” bill?
This “accounting and taxation” interview question deals with the concept of “e-way bill”. It is mainly referred as an “electron way bill” that is generated on the “e-waybillgst.gov.in” bill “portal”. This is an important document which is to be carried out by the “transporter” who supplies the “goods”. This is mainly to be generated for “transporting goods” whose value becomes more than Rs 50,000. It can be generated by the “supplier” or by the “recipient” who is basically in the form of an “unregistered person”.
This has simplified the process of “transportation” of the goods especially when it is “interstate supply”. It contains the details of the “consignee and consigner” which also contains the address of the “delivery place”, “value of the goods” and location of the “delivery place and date”.
Q19. Mention about the “Golden Rules” in “Accounting”?
“Accounting and Taxation” have their own set of “golden rules” which are based on “debit and credit”.
The “Golden Rule” states that:
- “Debit the Receiver and credit the giver”.
- “Debit what comes in and credit what goes out”.
- “Debit all expenses and losses and credit all income and gains”.

Q20. What is “Deterred Tax” and how is its value created?
In “accounting and taxation” terms, a “deterred tax” is mainly referred to an “asset” whose “tax amount” is paid or “carried forward”. This value which is “carried forward” cannot be identified in the “income statement”.
The value of such is mainly created by taking into consideration the difference that exists between the “taxable income” and the “booked income”.
Q21. A company is showing “positive cash flows” still it can be in trouble. What does this mean?
This “accounting and taxation” question is a bit “derogatory”. “Positive Cash Flows” does not guarantee the “success factor” of the company. If a company shows any kind of “unsustainable improvement” in its existing “working capital” it only means that the company is suffering from the “inefficient revenue”.
So “positive cash flows” does not mean that the company is out of trouble.
Q22. What do you mean by “GST Returns”?
This “accounting and taxation” interview question mainly deals with the concept of “GST Returns”. It is a document that is “filed” by the “taxable person” in the “current financial year” that is to be presented before the “tax authorities”. These documents mainly include:
- “Purchases”
- “Sales”
- “Output GST” that is to be levied upon sales
- “Input tax credit” that is mainly a “GST payment” that is imposed on the purchases
The concept of “GST” is normally “destination based”. With the invent of this “tax regime” the “indirect tax structure” got simplified, that has made the framework more efficient by digitalizing the entire “tax structure”. As a result of this “tax”, it has increased the level of competitiveness. The introduction of “GST” has broadened the “tax base” by bringing higher level of uniformity in the taxation system.
This “tax” is mainly collected to bring welfare in the “public finance expenditures”. The imposition of “GST” has brought “assurance” and has also developed a “progressive tax system”. This is also called as the “One Nation, One Tax System” which has brought “cooperation” as well as “coordination” in the “tax system”.
Q23. What is a “Bank Reconciliation Statement”?
This “accounting and taxation” interview question deals with the concept of “Bank Reconciliation Statement”. It is defined as the process of identifying the “transactions” on an individual basis. It also states matching the “transactions” with the “bank statements”. Doing this the “balance of the bank” matches with the “bank statement”. In this process the “transaction” that does not matches suitable “adjustments” need to be initiated for matching with the “financial statements”.
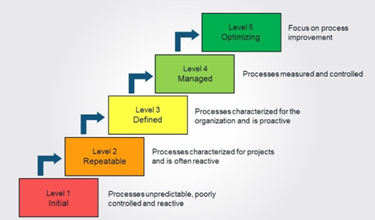
Q24. What is “CMM”?
“CMM” is known as the “Capability Maturity Model”. It is mainly a document that provides a structure to the basic “six elements” concerning “infrastructure”. This is used to measure the “effectiveness and capability” of the existing “finance structure” of the organization.
Q25. What are the ways to find out the “bad debts”?
“Bad Debts” can be determined by following the three ways:
- Percentage of the “Outstanding Accounts”.
- “Analysis of the aging”.
- “Credit Sales Percentage”.
Q26. What is the main difference between “capital and revenue transaction”?
“Capital Transactions” mainly deal with “large purchases of fixed assets” which are mainly used for generation of “revenue” over a “longer period of time”. These are also referred as “revenue transactions” which depend on the “acquisition” of “operating expenses”. These “expenses” are also termed as the “short term expenses” which are incurred in the “daily business operations”.
On the other hand, the “revenue transactions” mainly deal with the “incur” of the “short term expenses concerning the “current period” or within one year. These are needed to meet the “ongoing operational cost” of the business and thus are referred as the “operating expenses”.
Q27. What are “Fictitious Assets”?
This “accounting and taxation” interview question deals with “Fictitious Assets”. These are normally “intangible” and the benefits derived are determined for a “longer period of time”. These are normally “fake assets” which have o “physical presence”. These “assets” normally exist because they are considered to be a “major expense” for the business. These assets are normally “amortized” over the time which expands more than a “financial year”.
The examples of such “assets” are, “goodwill”, “deferred revenue”, “rights”, “preliminary expenses” and “accumulated losses”.
Q28. What is “double entry bookkeeping” and what are the rules?
“Double-entry bookkeeping” is an accounting system which states that for every “entry” made into one account an “equal entry” should be made into another “account”. The main purpose of “double entry bookkeeping” is to create a certain set of “financial statements” which is based on the preparation of “Trial Balance”. The “profit and loss” statement prepared shows the demarcation of the “revenue”, “costs” and the “profit and loss” incurred over a certain period.
The “double entry bookkeeping” is based on the following formulae:
“Assets = “Liabilities + Equity”
The rules of “double entry bookkeeping” are mainly divided into three main accounts. These accounts are:
- “Personal Accounts” states that the “receiver” should be “debited” and the “giver” should be “credited”.
- “Real Accounts”, states that “debit what comes in” and “credit what goes out”.
- “Nominal Accounts” states that all the “expenses and losses” should be “debited” and all the “income and gains” should be “credited”.
Q29. What does the “dual aspect” concept mean in accounting?
The “dual aspect” concept in “accounting” indicates that each and every “transaction” which is made by a business makes an effect in the business from two different aspects that are “equal and opposite” in nature. This concept forms the basis of the “double entry accounting system” which is used by all the “accounting frameworks” for the purpose of generating “accurate and reliable financial statements”.
An example of “dual aspect” of accounting can be seen from below:
A started business with a “capital” of Rs 5, 00,000, which is a “primary investment”. Now this “investment” would have the following effect on the business.
- First it would increase the “assets” of the business by Rs 5, 00,000 as a result of which the “cash increases”.
- “Capital” of the business would increase by Rs 5, 00,000.
Q30. What are the major “restraints” which can hamper the “financial statements”?
The “obstructions” that can hamper the “financial statements” are:
- No balance between the “benefit and the costs”.
- Delay leads to “irrelevant information”.
- No balance seen between the “qualitative characteristics”.
- No clarity in presenting the “true and fair view” of the accounting statements.
Conclusion
On a whole the candidate should know the topic well which would include an “extensive research”. This also includes knowing individual “job description” which would also specify the “job requirements” for the position in which the candidate is mainly applying for. It is also important to be clear about the role in which the application is mainly processed for. The “interviewee” should maintain a positive attitude which would not at all disclose about the personal problems that the candidate is facing in real life as this attitude can ruin the relationship and can disrupt the relationship. When the candidate would talk with the interviewer it is important to “speak with a clear voice”. The candidate should also be patient and wait for the turn and lastly the candidate should maintain a formal attire.












very useful blog it really amazing
Thank You for Sharing This Site List, Sunny!
It will help a lot 🙂
I impressed you for sharing this accounting and taxation interviews questions
Thanks for sharing Artice.keep sharing
I never expected to learn this many facts from your article. This truly is a great way to learn about the new and unexplored topics in an understandable way.
I have been looking for a proper article to learn about the basics of this topic and I tried several options as well but none of them explained the topic better than this article.
I used to have very little idea on the accounting coaching center and reading this blog post helped me in collecting about newer details and specifics about each one in detail. Thank you for this amazing share.
This is one of the articles that does not waste time and delivers the details as it promised. I can easily relate to all the points mentioned here. The article is precise which makes it easier to grasp the concept of the Accounting and taxation interview Q/A.
Hi, I want to achieve BAT certification, could you please guide me with the process
Hello!
I am Currently persuing graduation from B.com
I want to join BAT Course. Plz tell me What is The eligibility and fee structure
This website is an excellent resource for individuals seeking answers to their accounting and taxation questions. It provides comprehensive and reliable information, helping users navigate complex financial matters with ease. A must-visit for anyone seeking clarity in the world of accounting and taxation.
The Accounting and Taxation Questions section on this website is a goldmine for knowledge seekers. The variety of topics covered and the detailed answers provided make it an excellent platform for professionals and students alike. Highly recommended.
The accounting and taxation questions on this website offer practical insights and solutions. The user-friendly interface makes it easy to navigate and find relevant information. A great resource for students, professionals, and anyone interested in enhancing their knowledge in this area.