In this Pandemic, we have seen so many people lose their jobs. We realised that the lack of our skillset is the talking point for our lost jobs. People worked out on alternative courses to upgrade or begin a new career as per the market need. The World is changing so fast; I favour the hunger of upgrading our skills and ourselves to build your career graph towards high ranking. If you are preparing to upgrade your career in Quality management, here are some courses you can learn about them and how they have created a revolution in the business process. Here in this article, you will be introduced to the methodologies of Lean, Six Sigma and Lean Six Sigma.

Lean method
What is Lean?
Lean is a management tool for delivering values and optimising workflows in any business or production process. The topmost priority of Lean management is delivering high quality and customer satisfaction.
Lean concepts focus on
- Deliver value from the standpoint of the customer.
- Continuous improvement in the work process.
- Eliminate wasteful steps.
Benefits of Lean
- Increase in productivity and efficient workforce since it eliminated unnecessary activities.
- Lean management improves focuses on tasks that produce value.
- It reduces the process in cycle time (work in progress/Throughput).
- Improve uses of resources by operating as per the demand of the customer.
History of Lean Management
Lean management is derived from the Toyota production system, established in the late 1940s. The term Lean was invented by John Krafcik(CEO of Google’s self-driving car project, Waymo). Toyota put the foundation on two pillars: Respect for people and continuous improvement. The primary aim of Lean manufacturing was to reduce the practices that do not bring value to the product.
Following this process, there was a noticeable improvement in productivity, the efficiency of the employee, cycle time and cost-effectiveness
What is ‘Value’ in Lean Management:
We can define value as everything the customers will pay for. Value and Waste are the concepts used in the workflow’s improvement.
Cost Model: Value of the customer (V)=Performance (P)/Cost (c)
The Toyota 3M Model:

Toyota has developed its production system by eliminating the obstacles
- MUDA (Waste)-It refers to a waste that does not add value to the creation of the product or the customer will not pay for it. When there is a consumption in any activity, money, time and resources but add no value to the end product, it is MUDA.
The eight wastes in Lean Manufacturing- (DOWNTIME is the acronym of the eight wastes. )
1. Defect– It occurs when the product is not fit for use and results in rework.
2. Overproduction– Produced before the most downstream process or inaccurate demand information requires them.
3. Waiting– It is the opposite of overproduction. Waiting results from poor process communication and setup time.
4. Non utilized talent– This type of waste fails to ensure that all their potential employee skills are being utilized. Assigning wrong tasks will lead to poor management.
5. Transport– Unnecessary transfer of product from one place to another. Common types of transportation waste are multiple storage facilities and poorly designed production systems.
6. Inventory– The holding cost made it a form of waste. Examples of inventory are overproduction of goods, delay in production and inventory defects.
7. Motion– Unnecessary movement of a person or machine to operate a work. Lack of production standards and poor production planning are examples of motion waste.
8. Excess processing- It is a sign of a poorly defined process. It may result from a lack of communication, overlapping areas of authority, data redundancy, and human error.
- MURA (Unevenness)- When there is instability in business operations, it leads to fluctuation in production. The Uneven process can make the employee overworked in the peak season to meet the high demand and then become idle after the demand drops. The changes in the employee’s workload can lead to work in the process of inventory accumulation and defects and waiting in the workflow.
- MURI (Overburden)- This refers to putting too much stress and strain on the employees and machines. To fulfil the targets, machines and employees work more than their capacity. Because of this variation, Muri leads to Muda.
The Five Principles of Lean
- Identify Value- The first principle states to add value to the customer’s needs and requirements. To uncover the actual need of the customer, techniques like surveys, web analytics, interview, and information are used.
- Map the Value stream- This is the second step in the process to recognise all the activities necessary to complete the project properly. Mapping the entire workflow helps to identify the areas of inefficiencies and eliminate unwanted activities to deliver the best value to the customer and company.
- Create Flow- The principle pushes towards a smooth flow of the process to deliver a product. In Lean, waiting is a waste, so detect and remove the process, which is creating a roadblock.
- Establish Pull- Maintained inventory should be followed. Excessive inventory means an increase in costs and waste. This principle deals with wastes and values in lean inventory. They pulled work when there is a demand and optimised resources capacity to deliver the products.
- Continuous Improvement- The ultimate principle is all about perfection in the management. There should be uncompromising and endless surveillance of perfection in the work.
Some Important Lean Tools
- 5 S-. The five s stands for Sort, Set, Shine, Standardise and Sustain. This system improves workplace efficiency and effectiveness by.
- Removing unwanted items. (sort)
- Modify each work area to maximise productivity. (Set)
- Evaluate each work to find and eliminate issues before they become critical. (Shine)
- Recording the improvements so it can apply them to another work area. (Standardise)
- Repeat of each step to establish continuous improvement. (Sustain)
2. Kanban- Is implemented to qualify a clear flow without excessive planning or inventory. Kanban is a guide to a prior process of what to make and when.
3. Value Stream Mapping(VSM)- A method to analyse processes and identify obstacles in the work area.
4. Kaizen– This is a system that undertakes continuous improvement across different sectors as company culture, leadership, process, productivity, quality, safety and technology.
5. Jidoka- An idea to examine the production issue in the middle of the process rather than at the end. It helps to discover the root cause and fix the problems.
6. Just-in-time- This is an on-demand system that allows the manufacturer to produce after a customer needs a product. stock up on unnecessary inventory is not needed.
7. SMED(Single-Minute Exchange or Die)- The aim is to identify all changeover tasks within 10 minutes. Analyze each step in one minute or less. Reducing setup will improve efficiency.
8. Poke Yoke- This is a tool invented because of human error. Humans that perform repetitive tasks can make common mistakes and defects. Automation was the only solution to improve the manufacturing process.
9. Heijunka- It means ‘levelling’ the type and quality of production. Focus is to reduce capital costs, production time and inventories.
Six Sigma
What is Six Sigma?
Six Sigma is a data-driven and statistical methodology to improve quality by measuring the defect. This helps to increase the performance, profits and quality of the product. The goal of this methodology is to create a continuous process of improvement with fewer defects.
There are some tools used by the Six Sigma experts to improve the process, like Control Chart, Failure Mode and Effect Analysis(FMEA), Statistical Process Control(SPC), etc.
History of Six Sigma
Carl Friedrich Gauss (1777-1855) introduced the basic concept of Six Sigma as a measurement standard. In 1986, Bill Smith and Mikel Harry, two engineers of Motorola, developed Six Sigma.
Six Sigma principles
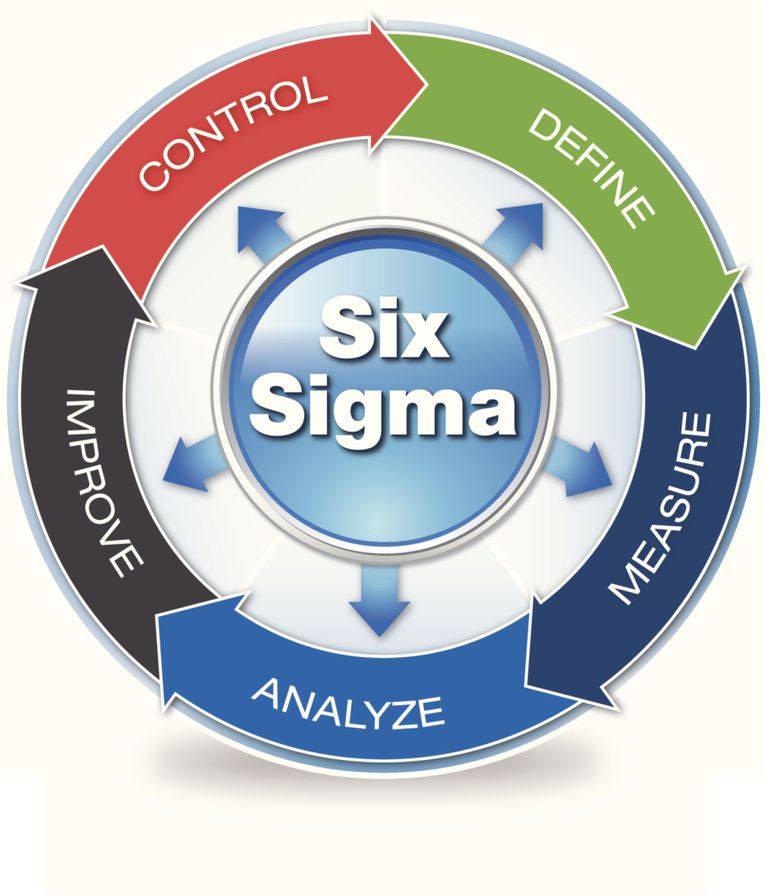
The five fundamental principles of Six Sigma.
- Customer Focus- The objective is to maximise the benefits for customers. To increase the sales of a company, a business must understand the demand of the targeted customer.
- Reduce defects- The target of Six Sigma is to achieve a defect rate of fixed standard deviation or 3.4 defects per million goods.
- Quality- The primary goal of Six Sigma is quality management. The quality-related focused areas include the elimination of defects and reduction of waste involved in the manufacturing of goods.
- Improve productivity- Increases in process productivity will bring profit to the organisation. Six Sigma reduces the cycle time (time takes to complete a work process). It also eliminates the work areas that do not add value.
- Involve Stakeholders- A successful process needs good teamwork, where stakeholders and trained people will collaborate to find solutions to complex issues.
Six Sigma Methodology
Two improved methods used in Six Sigma
- DMAIC (Define, Measure, Analyse, Improve, Control)
- DMADV (Define, Measure, Analyse, Design, Verify)
A step-by-step breakdown of –
DMAIC- It is used to correct the process that already exists
- Define- Describe the problem and aim of the project.
- Measure- Assess the current performance.
- Analyse- Control the root cause of any defects.
- Improve- Identify the defect and rectify the process.
- Control- Guide the future process of performance.
DMADV- It is used to create a new process
- Define- Describe the problem and objective of the project.
- Measure- Assess the current performance.
- Analyse- Control the root cause of any defects.
- Design- A process is created to fulfil the customer expectations.
- Verify- Check on the process which was designed to meet the customer’s needs.
Lean Six Sigma

What is Lean Six Sigma?
Lean Six Sigma is a managerial approach to improve business performance by eliminating wastes and defects. It is a combination of Lean and Six Sigma strategies. Lean principles focus on reducing wastes whereas Six Sigma targets variation-reduction in the work process.
Key elements of Lean Six Sigma
1. Customers- They are the focus of a business.Lean Six Sigma centres on better performance, on-time delivery, trustworthiness, proper transaction process and more. At every level, customer requirements are significant for a successful business.
2. Process- In a business, one must look out the business life cycle from the customer perspective, what you want. Applying the knowledge it will be easy to identify the areas where to add extraordinary value or improvement if any. This idea will help to improve efficiency and customer loyalty.
3. Leadership- Lean Six Sigma involves all employees to solve fresh problems within a company. It creates a sense of self-importance and a proactive attitude among the employees.
Benefits of Lean Six Sigma
1. Enrich customer satisfaction- Customer satisfaction is a factor that determines the success of an organisation. They will stay loyal as long as there is satisfaction with the products. Lean Six Sigma improves the quality and delivery methods of the products. Therefore, increased customer satisfaction will lead to an increase in sales.
2. Reduced costs- Reduction in defects and minimising waste, resulting in a low cost of production. Creating a substandard product can drive-away the loyal customers.
3. Better time management- Lean Six Sigma methodology helps their employees to manage their time appropriately. Employees become more creative and efficient at their work. They implemented principles of Lean Six Sigma in learning, performance and fulfilment.
4. Helps in strategic planning- It provides an important role in providing Enterprise level strategic planning. After setting the business goal, they conduct a SWOT analysis to focus on areas for improvement.
5. Talent advancement- Lean Six Sigma makes every employee understand the principles and practical application of the techniques. This enriches a talent in the people and sets a continuous learning culture within the organisation.
Traps to avoid
- Lack of knowledge of each tool before using them for the purpose.
- Poor physical planning of an organisation.
- Not upgrading with the current trends in the learning process.
- Lack of change of the goal between the organisation and individual.
- Applying Lean Six Sigma in all solutions without judging the situation properly.
Principles of Lean Six Sigma
1. Focus on the customer- The purpose of every company is to deliver a product as per customer satisfaction. For every company, the customer is the priority. Successful companies deliver value defined by the customers’ needs.
2. Mapping the value stream- It is necessary to figure out the root cause for the complete realisation of the actual working process. Analysing the collected data will show the specific problem area.
3. Eliminate variation- After identification of the problem, it’s time to eliminate the opportunities for defects. Removing the waste can achieve quality control and efficiency.
4. Teamwork- There is a requirement to train the leaders and team members in Lean Six Sigma, to know the goal of the project and its progress. Motivate the employee to solve the problems by using group thinking techniques.
5. Environment for flexibility and responsiveness- Lean Six Sigma can cause a tremendous change in management. During the process, that is identified as inefficient are changed. Change is uncomfortable but challenging as well.
Lean Six Sigma Belts
In the Lean Six Sigma hierarchy, there are six belts level-
- White Belt(General understanding)- Program to make you understand how Lean Six Sigma works. Correct the use of Lean Six Sigma methodology to convey the related problems to those working on process improvement projects.
- Yellow Belt (Active contributors)- Yellow belt holders know the working process and can support process improvement projects.
- Green Belt (Project managers)- It is an intermediate program to prepare you to manage process improvement projects.
- Black belt (Strategist) – manage and lead project teams. Black Belt have experience in working with Lean Six Sigma and process improvement.
- Master Black Belt (Mentor)- This is a very advanced level of belt. Master black holder Can educate others and become a master in the domain.
- Champion (Supports and develops)- Champion should be a part of the organisation’s leadership team. They are created for nurturing and supporting Lean Six Sigma culture.
Lean Innovation Management
Lean innovation is a new idea focused on increasing efficiency by taking customers’ feedback and minimising waste in the product development process.
The main methodologies are –
- The capacity to discover new opportunities through the use of design thinking.
- The power to improve business solutions with fewer resources, learn and validate.
- The ability to reduce waste, make successive improvements and eliminate the bureaucracy.
Implementation of Lean Six Sigma
The steps of Lean Six Sigma-
- Lean Six Sigma must be part of the organisation’s goal and strategy. Lean Six Sigma requires full support from upper management.
- Resource allocation is important in Lean Six Sigma. It works best when there are trained employees at all levels who can lead project teams.
- They provide training to the Employees for better skills and knowledge. Implementation of Lean Six Sigma can only be successful when employees have quality training.
- Interpreting data for decision making of a business work process. It helps to decide which project to select for improvement and which resource is dedicated to the projects.
Why is Lean Six Sigma so popular nowadays?
There are several reasons behind the widespread use of Lean Six Sigma throughout the world.
First, it is the most updated version of the quality management approach, which can replace TQC, TQM, etc.
Second, it is a planned, scientifically proven and statistical method of management.
Third, Lean Six Sigma is responsible for providing resource full employees by the belt system training.
Fourth, many leading companies like IBM, Sony, Kodak, Nokia,
Philips electronics, among others Run Lean Six Sigma programs. Therefore, it is a well-proven program to run a successful business.
Difference between Lean and Six Sigma
Lean and Six Sigma both are systems for continuous improvement of the business. They have the same objectives but different strategies-
1. The goal of Six Sigma is to remove defects and waste, at the same time improving quality and efficiency in a business process. whereas Lean is used to innovate the manufacturing and production process.
2. There is a different approach to identifying the cause of the waste. In Six Sigma, waste appears from change within the process but in Lean, Waste is an unnecessary step.
3. Lean helps to increase process efficiency by highlighting speed and cost optimisation. Six Sigma focuses on quality improvement. It reduces variation using Statistical techniques.
Interested to enrol in the Lean six sigma certification course? check out the best institution in India.
Henry Harvin
Henry Harvin ranks number 1 in the Six Sigma certification course among Top 5 by Business standard and Best course news.com. There are many course options on quality management –
- Postgraduate program in Lean Six Sigma
- Master black belt, black belt, Green Belt and yellow belt
- Lean Six Sigma in IT course
- 5S course
- value stream mapping
- Advanced statistics for the six sigma course and many more.
What will you gain here?
- 9 in 1 course includes- High-quality training, Live projects, internship facility, certification, placement, E-learning, Boot camps, hackathons and Gold membership.
- An extensive curriculum designed according to ASQ.
- 100% practical training for all the courses.
- Lifetime support and access to LMS
- Training from the industry experts with 15 years of working experience, who will provide you with over 100 keynotes and 350 lectures.
- Gold membership benefits you with weekly 10 job opportunities, experience industry projects, interview skills, 1-year boot camp sessions.
course fees- Post-graduation program in Lean Six Sigma- 89000, Master Black belt- 59500, Black belt- 29500, Green Belt- 17500, yellow belt- 12500
Contact details– Ph no: 9015266266
Whatsapp: 9891953953
Email- [email protected]
–
Overview
In short, Lean Methodology aims at waste reduction in a process. Whereas Six Sigma aims at reduction of process variation and Lean Six Sigma helps to improve efficiency, optimising the resources and customer satisfaction.
Six Sigma and Lean Six Sigma starts with the Green Belt level, then Black Belt and Master Black Belt. So which level will suit as per the eligibility?
If you have job experience in some organizations, Six Sigma certification is a plus for getting a high position. Working on more than a project then you can opt for the Six Sigma Black Belt Certification. People with no experience can take the Lean Six Sigma Green Belt or Black Belt certification. If you wish to train professionals, consult on a project then Master Black Belt on Six Sigma or Lean Six Sigma certification is a must.
Now regarding the right accreditation body, it is suggested to choose the institution which provides a certificate under:
- The American Society for Quality(ASQ) for Six Sigma certification
- The International Association of Six Sigma Certification (IASSC) for Lean Six Sigma certification.
‘Lean six sigma course is a bedrock of transformation program’ what is your opinion?
FAQs
Ans- You must be an ASQ certified black belt, have project leadership experience or completed 10 projects on Six Sigma.
Ans. It takes 10 weeks to complete Lean six sigma Green Belt, 8 Weeks For Lean principle and 16 weeks For Lean Six Sigma Black Belt.
Ans. A fresher can take the Six Sigma yellow belt and Lean Six Sigma Green Belt training certification.
Ans. The Black Belt examination as per the ASQ is a difficult one. It requires disciplined study, smart preparation and a strategy.
Ans. A Six Sigma certification is beneficial for both companies and individuals. completing the course, you will gain experience in project management and your career will get a new height.










Thanks for this info..well done
The blog about LEAN, SIX SIGMA, AND LEAN SIX SIGMA provided a great information..!! It was very helpful for me!